 Malaria
Malaria
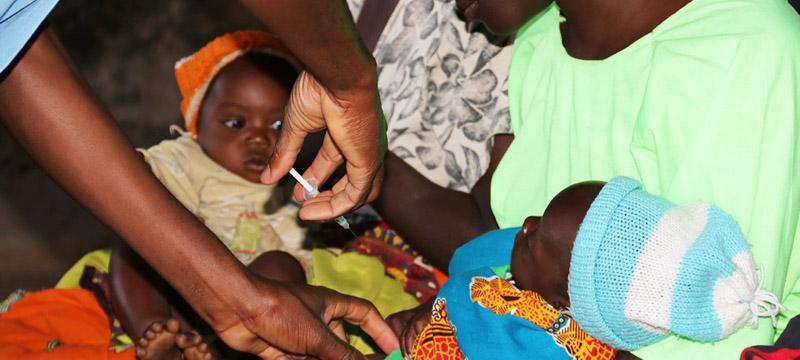
Fight against Malaria: World Health Organization approves second vaccine for children
The World Health Organization (WHO) on Monday recommended a new anti-malaria vaccine for children, a move that could offer countries a cheaper and more readily available option than the world’s first shot against the parasitic disease.
The R21/Matrix-M vaccine, developed by Britain’s Oxford University, can be used to curb the life-threatening illness spread to humans by mosquitoes, the WHO said, stating that “both vaccines are shown to be safe and effective in preventing malaria in children and, when implemented broadly, are expected to have high public health impact.”
It is the second malaria vaccine recommended by WHO, following the RTS,S/AS01 vaccine, which received a WHO recommendation in 2021.
According to WHO, malaria “places a particularly high burden on children in the African Region”, with nearly half a million children dying each year.
“As a malaria researcher, I used to dream of the day we would have a safe and effective vaccine against malaria. Now we have two,” said Dr Tedros Adhanom Ghebreyesus, WHO Director-General.
Unprecedented demand
Demand for malaria vaccines is unprecedented; however, RTS,S is in short supply. The addition of R21 to the list of approved shots is expected to result in sufficient supply to benefit all children living in areas where malaria is a public health risk.
Tedros described it as “a vital additional tool to protect more children faster, and to bring us closer to our vision of a malaria-free future.”
WHO Regional Director for Africa, Dr Matshidiso Moeti said the shot “holds real potential to close the huge demand-and-supply gap. Delivered to scale and rolled out widely, the two vaccines can help bolster malaria prevention and control efforts and save hundreds of thousands of young lives in Africa from this deadly disease.”
Next steps
WHO is now reviewing the vaccine for prequalification. Having got approval that will enable GAVI [a global vaccine alliance] and Children’s Fund UNICEF to buy the vaccine from manufacturers, added Tedros.
The vaccine will be rolled out in some African countries, including Burkina Faso, Ghana and Nigeria in early 2024, and will be available in mid-2024 in other countries, Tedros said, adding that doses would cost between $2 and $4.
According to Tedros, WHO approved the new malaria vaccine based on the advice of two expert groups: Strategic Advisory Group of Experts on Immunization (SAGE) and the Malaria Policy Advisory Group (MPAG).
Recommendation on dengue, meningitis
WHO also recommended Takeda Pharmaceuticals’ vaccine against dengue for children aged six to 16 living in areas where the infection is a significant public health problem.
Dengue, common in tropical and subtropical climates, is a viral infection spread from mosquitoes to people.
WHO’s advisory group SAGE also recommended that all countries in the African “meningitis belt” introduce what it described as (Men5CV) into their routine immunization programmes. It said a single dose scheduled at nine to 18 months of age should fight the disease.
WHO added that “in high-risk countries, and countries with high-risk districts, a catch-up campaign should also be conducted at the time of the introduction of Men5CV, targeting all individuals aged 1 to 19 years.”
Support Our Journalism
We cannot do without you.. your contribution supports unbiased journalism
IBNS is not driven by any ism- not wokeism, not racism, not skewed secularism, not hyper right-wing or left liberal ideals, nor by any hardline religious beliefs or hyper nationalism. We want to serve you good old objective news, as they are. We do not judge or preach. We let people decide for themselves. We only try to present factual and well-sourced news.







